Scientific Achievement
Tender APXPS results provide direct quantification of hydration on polymers in situ at the molecular level.
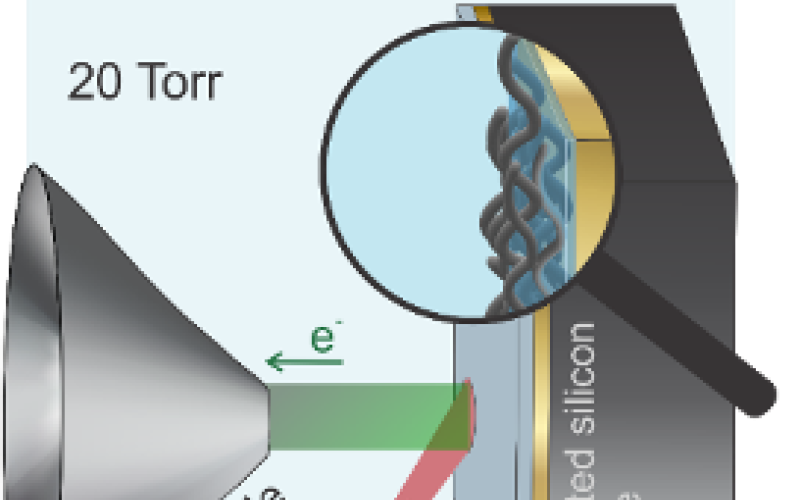
Image: Schematization of the hydration probing by APXPS under in situ conditions.
Significance and Impact
Our results facilitate the precise understanding and the correlations between functional group chemistry, counter ion, dissociation of ionic groups, and resulting amount of sorbed water near the surface.
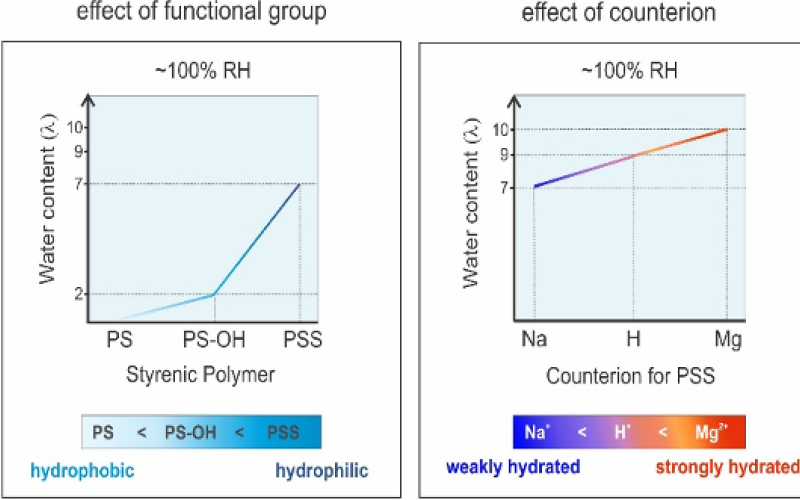
Left image: Effect of functional group on water content.
Right image: Effect of counterion on water content.
Research Details
- Experiments were carried out on model polymer systems of hydrophobic polystyrene, hydrophilic poly(vinyl phenol) and charged polystyrene sulfonate thin films.
- Interaction of water vapor with polymer surfaces were investigated in situ from UHV up to 100% relative humidity.
- APXPS results showed a direct relationship between the hydrophilicity and number of water sorbed.
- Additionally, counterion specific water sorption on polyelectrolytes were revealed and showed a direct relationship with the hydration number of counterions
Work was performed at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and University of California -Santa Barbara
P. Aydogan Gokturk et al., ACS Applied Polymer Materials (submitted)

